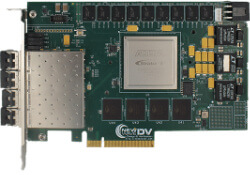
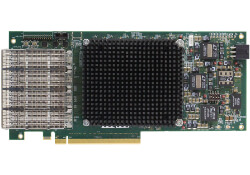
New Wave Design Products No Longer Recommended for New Design
New Wave Design creates products for long-term and long-duration industries, and produces those products for as long as possible. The list of solutions below have entered into a production phase beyond recommended new design incorporation.
Access technical information such as datasheets for these products below, and if you are in need of one of these products, please reach out to discuss procurement or alternative solutions.