How Are Ethernet Interfaces Implemented?
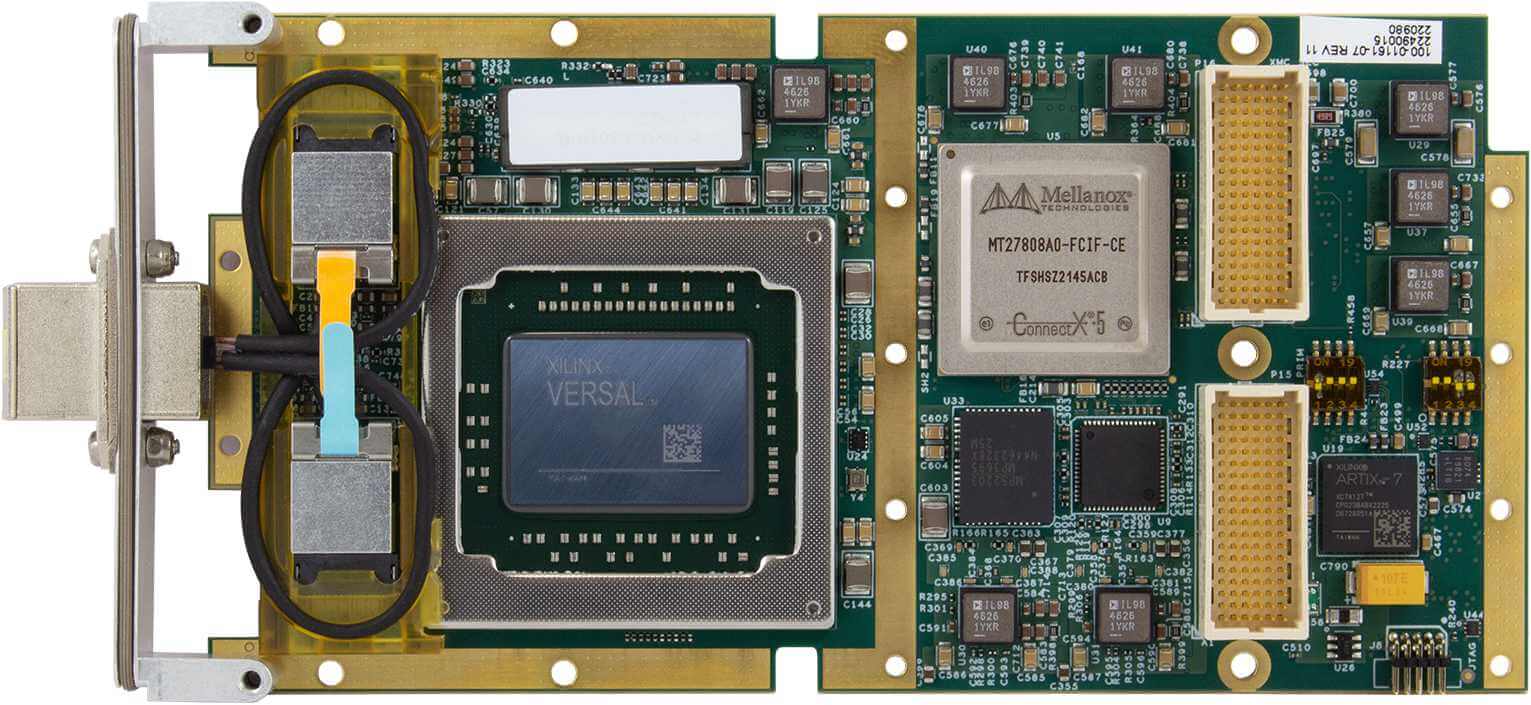
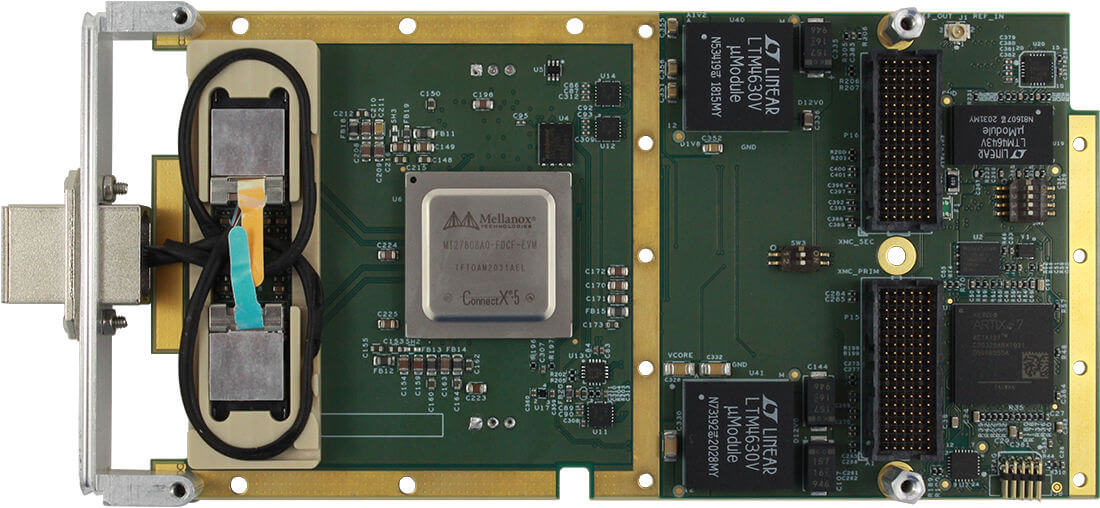
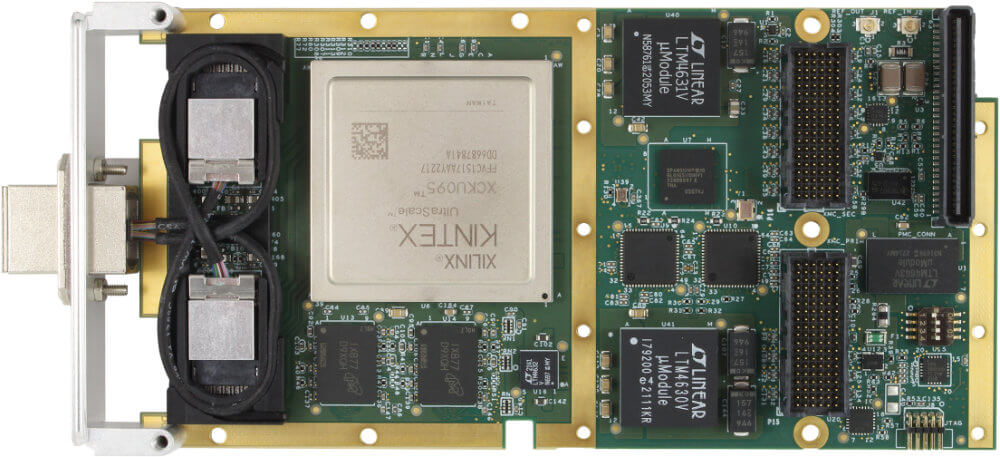
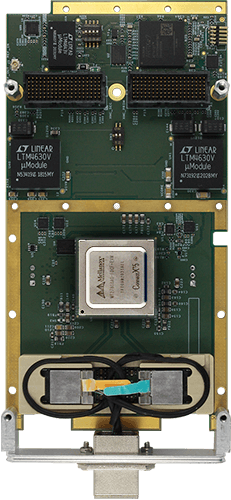
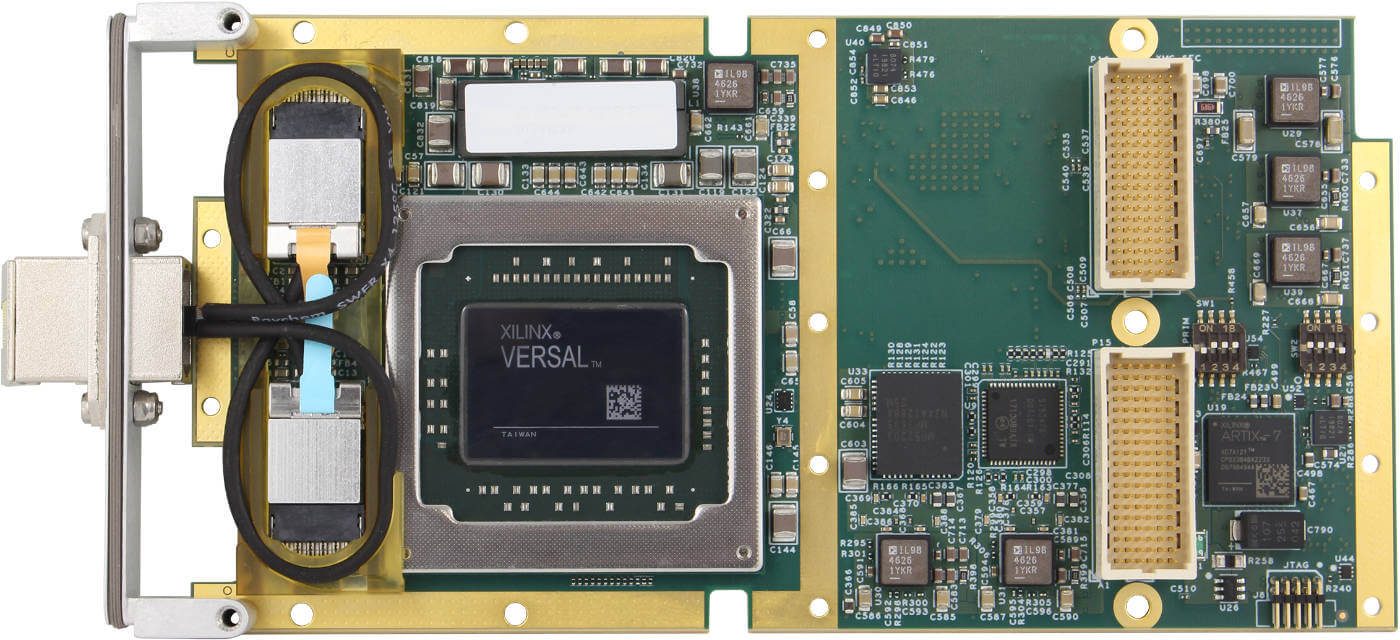
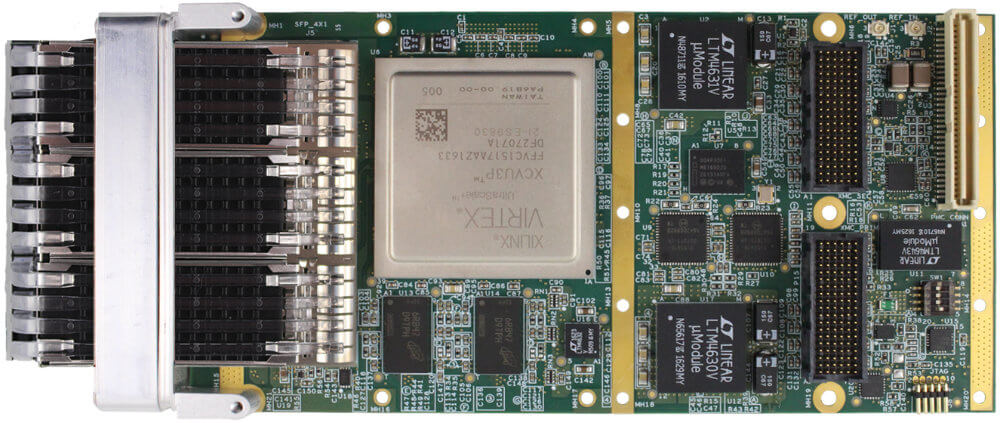
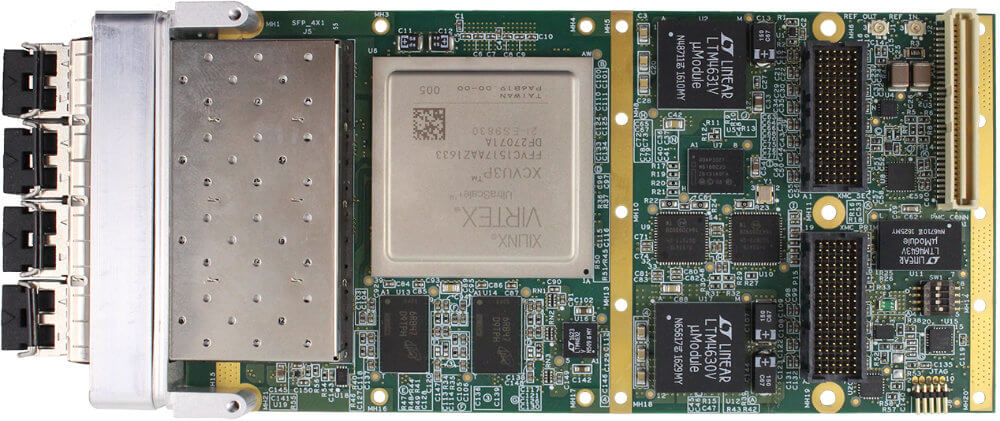
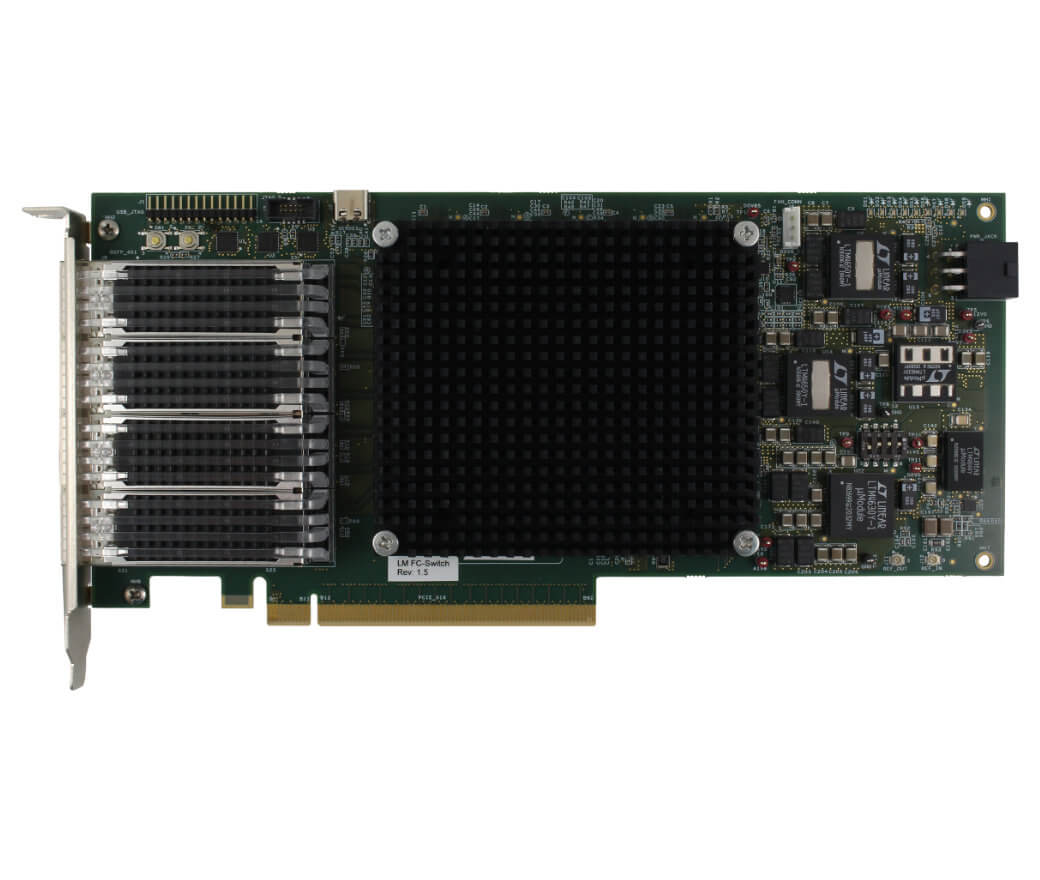
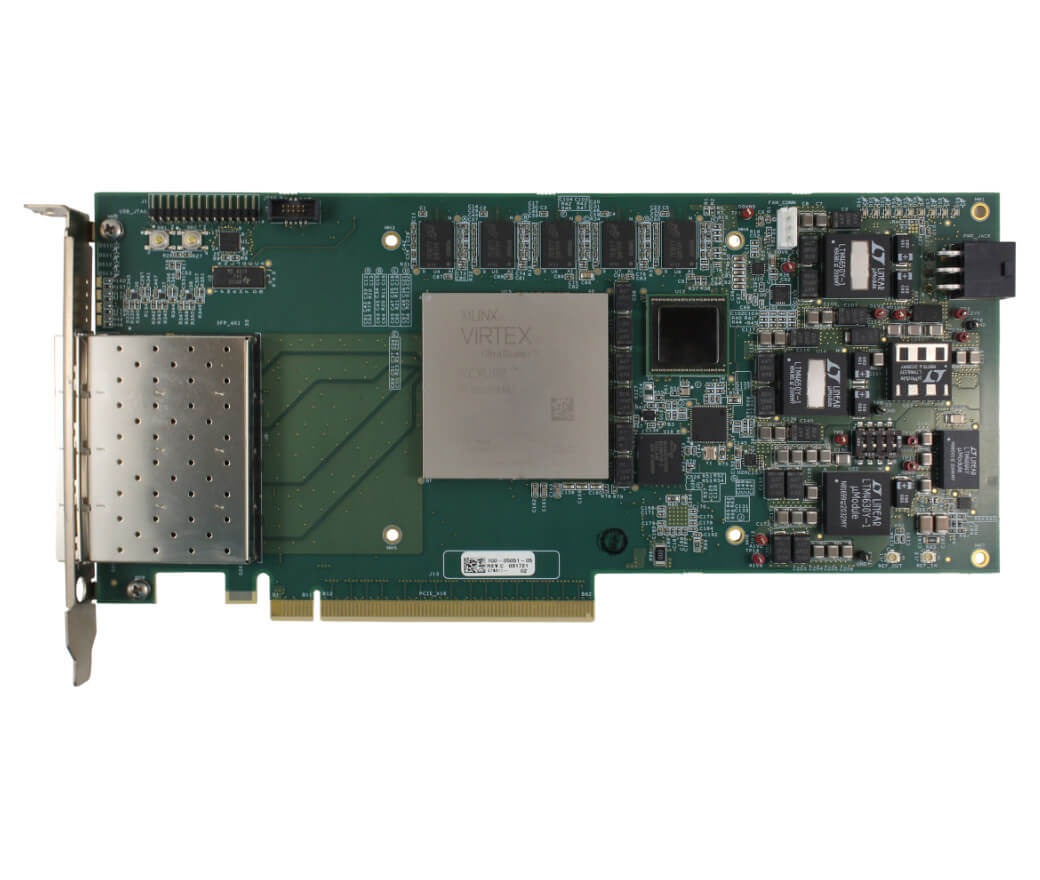
The Ethernet interfaces on an interface card can be implemented using multiple technologies. Dedicated Ethernet FPGA cards and ASIC-based cards are among the most common high performance implementations.
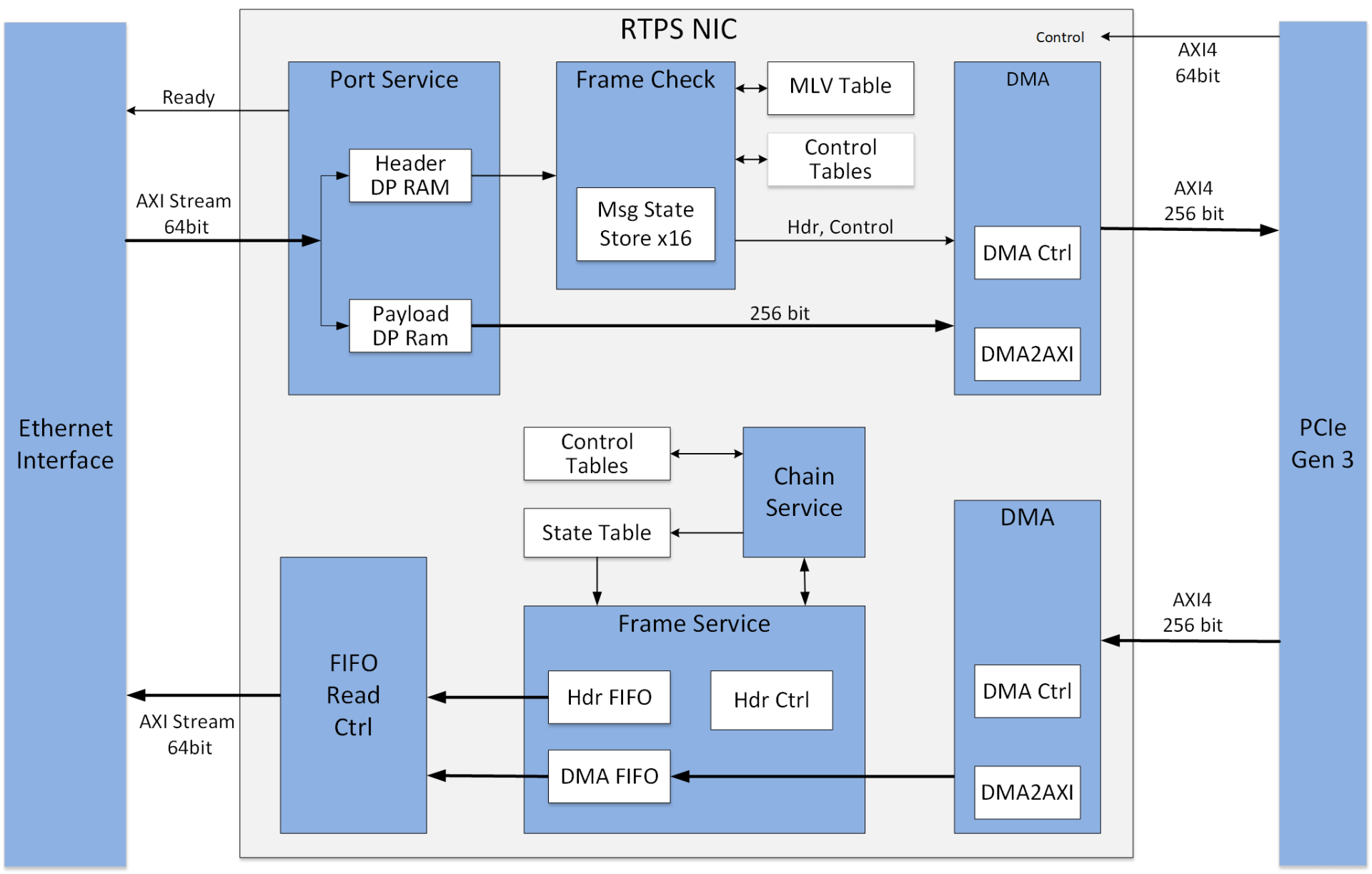
FPGA stands for Field Programmable Gate Array, a type of integrated circuit capable of being programmed by the user after initial manufacture. An FPGA card is a piece of hardware that contains one or more of these arrays alongside additional components like memory and power management. The main unique features of these cards are twofold:
- They can be programmed in order to carry out specialized industry and application-specific tasks like the management of sensor interfaces, the processing of real-time data or communication between various systems. As the FPGA is programmed by the user after initial manufacture, it is possible to offer ASIC hardware-level performance for low-volume applications where ASIC development would not be economically feasible.
- They offload processing weight from the CPU. The hardware-first nature of an FPGA card offers higher bandwidth and lower latency operations than software-based NICs when connecting to Ethernet. By offloading network processing tasks to the FPGA, CPUs are freed up to perform other tasks, leading to overall improvement in system performance.
The other common implementation technology is ASIC based. ASIC stands for application specific integrated circuit. An ASIC is a type of integrated circuit customized for a particular use. In this case, the ASIC is customized to offload as much protocol specific processing as possible.
Like FPGA based implementations, ASIC implementations offload protocol processing from the CPU. Unlike FPGA solutions, ASIC solutions have defined capabilities that can not be updated. That means a user’s requirements must fall within an ASICs capabilities, as ASICs do not offer the hardware-level customization available in FPGA-based solutions.
Ethernet Interfaces in Military, Aerospace and Defense Applications
The different types of Ethernet interfaces — especially when comparing high-performance ASIC and FPGA cards to standard, Layer 2 software-based NICs — matter most when you look at how they’re applied. Our cards are most commonly used in aerospace, defense and military applications where high-speed, low-latency requirements are mission critical.
It’s easier to understand the difference the right Ethernet interface card can make by learning about real-world applications. For instance:
- High-bandwidth Communication – Communication between avionics systems like radar, SIGINT, and countermeasures need rugged interface cards that can stand up to the temperature, shock, and vibration found in their intense environments while delivering large amounts of data between systems.
- Low Latency Communication – Latency is a high priority when you’re transmitting mission-critical sensor, surveillance and reconnaissance data. Being able to transmit and receive more data in less time means being able to act on the data faster, making the most of your missions systems.
- Heterogeneous Computing – FPGA cards programmed to support a specific sensor are capable of signal processing and data analysis in real time. This heterogeneous computing strategy makes it faster and easier to act upon data quickly.
- Application Processor Offloading – Protocol offloads enable CPUs and GPUs to focus on their application processing while leaving all protocol processing to the interface card. This enables greater compute performance out of the system’s CPU and GPU elements.